Kinney JP, Spacek J, Bartol TM, Bajaj CL, Harris KM, Sejnowski TJ (2013) Extracellular sheets and tunnels modulate glutamate diffusion in hippocampal neuropil. J. Comp. Neurology, 521:448-464. PMCID: PMC3540825. (8MB PDF)
Introduction
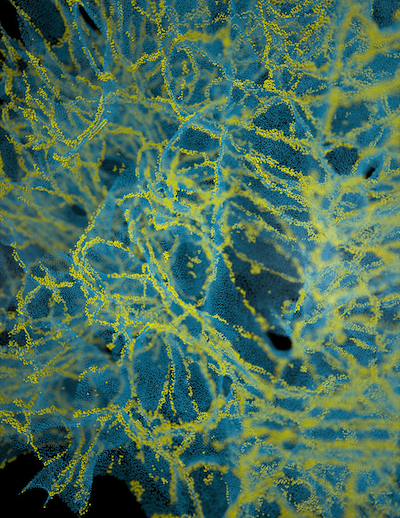
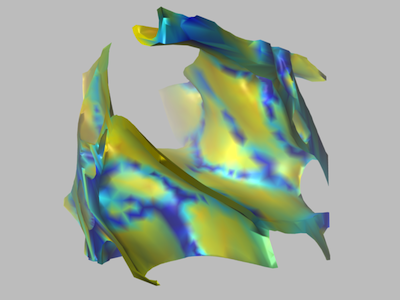
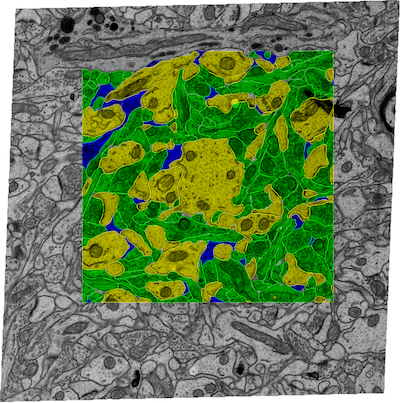
In the manuscript titled "Extracellular sheets and tunnels modulate glutamate diffusion in hippocampal neuropil", published in the Journal of Comparative Neurology, the authors present a reconstruction of the 3D geometry of 180 cubic microns of rat CA1 hippocampal neuropil from serial electron microscopy and corrected for tissue shrinkage. The reconstruction revealed an interconnected network of tunnels, formed at the junction of three or more cellular processes, spanned by sheets between pairs of cell surfaces. Tunnels tended to occur around synapses and axons and sheets were enriched around astrocytes. Simulations suggested that the rate of diffusion of neurotransmitter was slower in sheets than in tunnels.
Animation
Here is the "Waltz through the Hippocampal Neuropil" video.
Downloads
The following bzipped tar files contain the EM images, traces, 3D reconstructions, and software described in the manuscript. For more details about how the data was collected and the reconstructions were created, please refer to the paper.
EM Images
This file contains the EM images (.jpg) and the manually-traced contours of the cell processes in the images (Volumejosef). They can be viewed in Reconstruct.
Reconstructions
This file contains the surface meshes of the 3D reconstructions illustrated in Figure 2B-H in the manuscript. The mesh file is assumed to be in the Hughes Hoppe mesh file format which first psts the location of all vertices followed by a pst of faces that reference the vertices. Vertices are specified by a vertex index i and three coordinate positions; x, y, z: [Vertex i x y z]. Faces are specified by a face index j and three vertex indices; v1, v2, v3: [Face j v1 v2 v3]. All indices are positive integers larger than zero. For more information, see Chapter III, Section 2 of Kinney (2009).
Meshmorph
Meshmorph contains the source code for a program used to manipulate reconstructed surfaces. Static files can be downloaded here. This custom program written in c++ accepts a reconstructed surface as input. The program models the surface as a system of interconnected springs and and manipulates the location of the surface on the nanometer scale to reduce the potential energy of the springs. In this way, the program was used to control the morphology of the extracellular space. For documentation of the program see Chapter II, Section 1.F of Kinney (2009).
Meshalyzer
Meshalyzer contains the source code for a mesh analysis program. Static files can be downloaded here. This custom program written in c++ accepts a reconstructed surface as input, analyzes the geometry of the surface, and prints a summary report. For documentation of the program see Chapter 3 of Kinney (2009).
Information on this page originally appeared here on our collaborators' website.
Introduction
In the manuscript titled "Extracellular sheets and tunnels modulate glutamate diffusion in hippocampal neuropil", published in the Journal of Comparative Neurology, the authors present a reconstruction of the 3D geometry of 180 cubic microns of rat CA1 hippocampal neuropil from serial electron microscopy and corrected for tissue shrinkage. The reconstruction revealed an interconnected network of tunnels, formed at the junction of three or more cellular processes, spanned by sheets between pairs of cell surfaces. Tunnels tended to occur around synapses and axons and sheets were enriched around astrocytes. Simulations suggested that the rate of diffusion of neurotransmitter was slower in sheets than in tunnels.
Animation
Here is the "Waltz through the Hippocampal Neuropil" video.
Downloads
The following bzipped tar files contain the EM images, traces, 3D reconstructions, and software described in the manuscript. For more details about how the data was collected and the reconstructions were created, please refer to the paper.
EM Images
This file contains the EM images (.jpg) and the manually-traced contours of the cell processes in the images (Volumejosef). They can be viewed in Reconstruct.
Reconstructions
This file contains the surface meshes of the 3D reconstructions illustrated in Figure 2B-H in the manuscript. The mesh file is assumed to be in the Hughes Hoppe mesh file format which first psts the location of all vertices followed by a pst of faces that reference the vertices. Vertices are specified by a vertex index i and three coordinate positions; x, y, z: [Vertex i x y z]. Faces are specified by a face index j and three vertex indices; v1, v2, v3: [Face j v1 v2 v3]. All indices are positive integers larger than zero. For more information, see Chapter III, Section 2 of Kinney (2009).
Meshmorph
Meshmorph contains the source code for a program used to manipulate reconstructed surfaces. Static files can be downloaded here. This custom program written in c++ accepts a reconstructed surface as input. The program models the surface as a system of interconnected springs and and manipulates the location of the surface on the nanometer scale to reduce the potential energy of the springs. In this way, the program was used to control the morphology of the extracellular space. For documentation of the program see Chapter II, Section 1.F of Kinney (2009).
Meshalyzer
Meshalyzer contains the source code for a mesh analysis program. Static files can be downloaded here. This custom program written in c++ accepts a reconstructed surface as input, analyzes the geometry of the surface, and prints a summary report. For documentation of the program see Chapter 3 of Kinney (2009).
Information on this page originally appeared here on our collaborators' website.